SIMULATION OF A PERFECT DIELECTRIC DROP IN ELECTRO-OSMOTIC FLOW OF AN ELECTROLYTE THROUGH A MICROCHANNEL
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.18540/jcecvl3iss3pp294-319Palavras-chave:
Dinâmica de fluidos computacional (CFD), Gota dielétrica, Movimento eletro-osmótico, Solução eletrolítica, Micro canal.Resumo
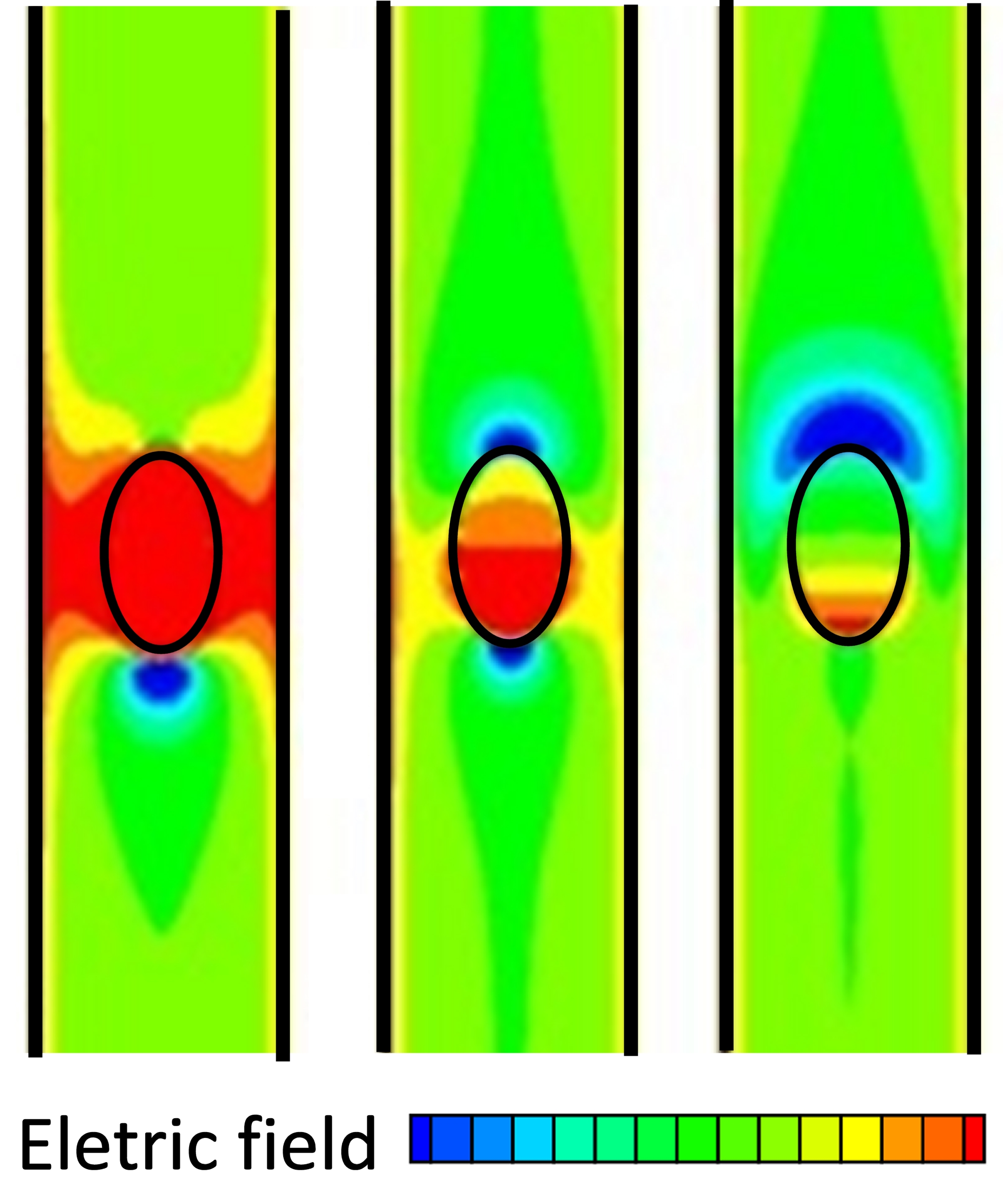
This research uses a computational fluid dynamic model to simulate motion and deformation of a dielectric drop in electrolyte solution in a microchannel. Wall charge density, the Debye-Hückel parameter and the Weber number are varied for uncharged, positively and negatively charged drop interfaces. Drop flow and deformation were analysed and the effects of charge distribution, electric field and permittivity jump were discussed. For a positively charged channel wall, negatively charged drops moved faster and positively charged drops moved slower than an uncharged drop. This effect increased for a higher We. Vortex flow was observed inside the drop. For a low surface tension, the drops were elongated due to electric forces acting on its surface with the charged drops deforming more than the uncharged one. When the permittivity component of the force was removed, the drop had a horizontal deformation that was sufficiently high to cause the negatively charged drop to break up.Downloads
Downloads
Publicado
2017-03-22
Como Citar
Magalhães Barbosa Felisberto, M., & Vianna Novaes de Carvalho Teixeira, A. (2017). SIMULATION OF A PERFECT DIELECTRIC DROP IN ELECTRO-OSMOTIC FLOW OF AN ELECTROLYTE THROUGH A MICROCHANNEL. The Journal of Engineering and Exact Sciences, 3(3), 294–319. https://doi.org/10.18540/jcecvl3iss3pp294-319
Edição
Seção
Transport Phenomena












